DVGW reference radiometer for UV drinking water disinfection
The German Technical and Scientific Association for Gas and Water (DVGW) and the Austrian standardization committee have defined the requirements for UV water disinfection systems with UV low-pressure lamps in DIN 19294-1:2020-08. This also specifies the design, function and opening angle of DVGW reference radiometers. The previous technical rule W294-3 and ÖNORM 5873 continue to apply to devices for drinking water disinfection with medium-pressure lamps. The sensors are inserted into a pressurized water-tight measuring window tube, which enables simple and reproducible replacement of the sensors.
With an aperture angle of 160°, our sensors are suitable for precise radiometric measurement of UVC irradiance in UV water disinfection systems. We offer these with reference radiometer RMD.
The RMD as DVGW reference radiometeris one of the latest developments from Opsytec Dr. Gröbel GmbH. This easy-to-use radiometer incorporates more than 30 years of experience in all areas of irradiance measurement.
It is characterized by a wide dynamic range and extremely low noise.
For this purpose, the sensor already contains a multi-stage amplification, an extremely precise analog-to-digital converter and a temperature sensor. The memory contained in the sensor contains all sensor identifications and the calibration history.
The use of suitable materials ensures excellent corrosion resistance and long-term stability. No ageing can be detected over a period of one year. The sensors are factory or DAKKS / ISO17025 calibrated.
TECHNICAL DATA DVGW reference radiometer sensor
| Spectral range | 240 - 290 nm |
| Measurement range, typ. | 0 - 200 W/cm² |
| Resolution | 0,001 µW/cm² |
| Dynamic range | up to 107 |
| AD conversion | 24 bit |
| Temperature sensor | integrated |
| Opening angle | 160° |
| Dimensions | Ø 20 x 60 mm |
| Optical area | Ø 15 mm |
| Weight | 160 g |
| Connecting cable | 1,5 m |
| Operation temperature | 0 to 60 °C |
| Storage temperature | -20 to 60 °C |
| Humidity | < 80% non-condensing |
| Calibration uncertainty | 5-7% (k=2) |
| Linearity error | < 1% |
| Aging / year | < 2% |
TECHNICAL DATA RMD DVGW reference radiometer
| Sensor connectors | 2, fully digital |
| PC interface | USB 2.0 (only RMD PRO) |
| Display | graphical, illuminated |
| Display output | 1 + 2 channels |
| Irradiance + Dose | |
| Min/Max Irradiance | |
| Dimensions | 160 x 85 x 35 mm |
| Weight | 250 g |
| Power supply | Li-Ion battery, USB |
| 100 - 240 V, 50/60 Hz | |
| plug-in power supply | |
| Internal memory | 8 GB (only RMD PRO) |
| Sampling rate | adjustable: 1 s - 15 min |
| Recording time | > 2400 h |
| Operation temperature | 0 to 60 °C |
| Storage temperature | -20 to 60 °C |
| Humidity | < 80% non-condensing |
Background to the use of DVGW reference radiometers according to DIN 19294-1 / DIN 19294-4 / DVGW W294-1 / OENORM
Lamps that generate UV radiation in the short-wave UVC spectral range are used for UV drinking water disinfection. According to TrinkwV §11, low-pressure mercury lamps and medium-pressure mercury lamps are approved for drinking water disinfection.
Low-pressure mercury lamps generate almost monochromatic radiation at 253.7 nm.
Due to their high output and high lamp pressure, mercury medium-pressure lamps generate a broad spectrum of UV radiation during operation, including UV-C radiation, which is required for the disinfection of water.
The DIN 19294-1:2020-08 standard not only specifies the requirements for devices with low-pressure mercury lamps for UV drinking water disinfection and their DVGW sensors for UV drinking water disinfection systems, but also defines precise specifications for their calibration.
The technical rule DVGW W294-3 and ÖNORM 5873 continue to apply to devices for drinking water disinfection with medium-pressure mercury lamps.
During operation, the irradiance in UV drinking water disinfection systems must be continuously monitored in order to monitor ageing, failure and contamination. Both lamp types require regular checks and reference measurements to maintain their effectiveness.
Device sensors that are exposed to UV radiation are subject to an ageing process and must be checked and calibrated regularly. Reference radiometers and sensors with the same measuring field angle and valid calibration are suitable for this purpose and are used by waterworks personnel to carry out regular comparative measurements on UV devices in operation.
The old technical rule DVGW W294-1:12/2023 also specifies requirements for sensors and reference measurements in order to ensure the performance of these lamps in drinking water disinfection.
Compared to the last edition the new changes are:
- regular calibrations (annually)
- Intervals for reference measurement (monthly)
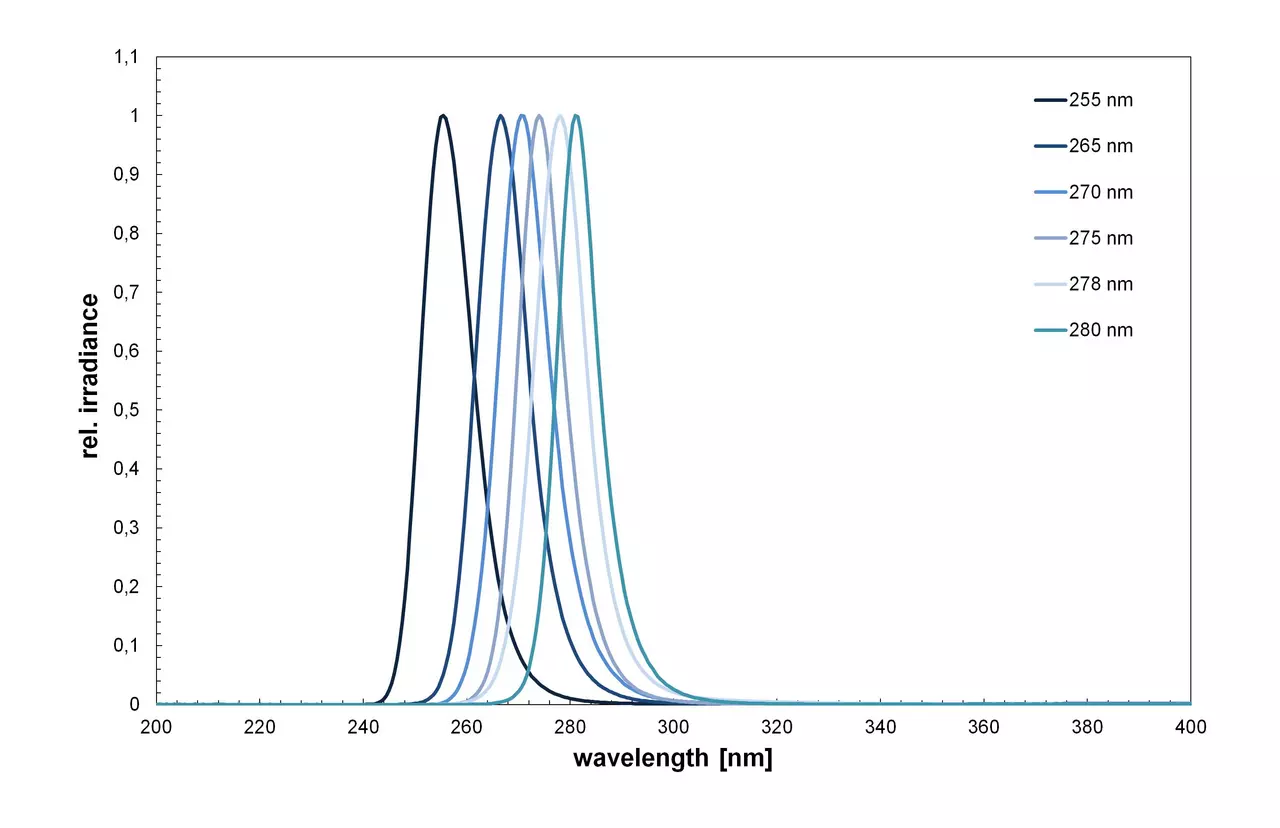
TYPICAL UV SPECTRES for UV drinking water disinfection in accordance with DIN 19294-1 / DIN 19294-4 / DVGW W294-1
While mercury vapor lamps are a proven technology, UVC LEDs are increasingly becoming an alternative for UV drinking water disinfection due to their mercury-free nature and the latest advances in efficiency and radiation flux. The first pilot systems have already been installed and the latest research results show that the UVC LEDs used are very effective. UVC LEDs use special semiconductors to generate UV radiation.
Their emission is narrow-band, with the wavelength and radiation flux depending on the manufacturing process and the resulting binning. UVC LEDs can be precisely controlled. Not only the device technology, but also the standard for defining device characteristics and determining disinfection efficacy for UVC LED devices in public drinking water supplies is currently being developed.
In summary, reference measurement and calibration are becoming increasingly important. Calibration of DVGW sensors is already critical to ensure accurate measurement and control of the UV radiation required for UV disinfection of drinking water.
Only appropriately calibrated sensors and reference radiometers may be used for UV devices with one type of lamp and sensor (same design and same type of calibration lamp).
Regular calibrations in accordance with the standard specifications of DIN 19294-1:2020-8 / DIN 19294-3:2020-8 ensure the accuracy of the sensors, which in turn ensures reliable monitoring and control and thus effective and safe drinking water disinfection.
We can calibrate DVGW sensors to these lamps in our laboratory:
- Low-pressure mercury lamps (253.7 nm)
- Mercury medium-pressure lamps (240 - 290 nm)
- UV LEDs (255, 265, 270, 275, 278 and 280 nm)
To this end, we are accredited as a calibration laboratory for UV sensors and as a testing laboratory for spectrometers, spectroradiometers and light sources in accordance with DIN EN 17025:2018. Our accreditation according to this international standard confirms our competence and reliability in carrying out precise calibrations and tests. We ensure the highest quality standards in the testing and calibration of UV sensors as well as the testing of spectrometers, spectroradiometers and light sources to deliver accurate and trustworthy measurement results.
Downloads
What aperture angle do the DVGW sensors have?
The DVGW sensors for the reference radiometer have an aperture angle of 160°.
Is there also a version with a 40° aperture angle?
No. The 40° version of the DVGW sensors is obsolete and is no longer available.
How often do DVGW reference radiometers need to be calibrated?
We recommend calibration every 12 months.